Оптимизация входных трубопроводов TensorFlow для пиковой производительности
30 июля 2025 г.Обзор контента
- Резюме лучшей практики
- Воспроизведение фигур
- Набор данных
- Итерационная петля
- Метод графика
- Используйте обертки для функции сопоставления
- Сравнение трубопроводов
- Оптимизированный
Резюме лучшей практики
Вот краткое изложение лучших практик для проектирования входных трубопроводов Tensorflow:
- Используйте
prefetchПреобразование, чтобы перекрывать работу производителя и потребителя - Параллелизировать преобразование считывания данных, используя
interleaveтрансформация - Параллелизировать
mapПреобразование путем установкиnum_parallel_callsаргумент - Используйте
cacheПреобразование в данные кэша в памяти во время первой эпохи - Векторизировать пользовательские функции, передаваемые в
mapтрансформация - Уменьшить использование памяти при применении
interleaveВprefetch, иshuffleпреобразования
Воспроизведение фигур
Примечание:Остальная часть этого ноутбука о том, как воспроизводить вышеупомянутые фигуры. Не стесняйтесь поиграть с этим кодом, но понимание, что он не является неотъемлемой частью этого урока.
Чтобы пойти глубже вtf.data.DatasetПонимание API, вы можете играть со своими собственными трубопроводами. Ниже приведен код, используемый для построения изображений из этого руководства. Это может быть хорошей отправной точкой, показывая некоторые обходные пути для общих трудностей, таких как:
- Время исполнения воспроизводимость
- Намеченные функции Желающие выполнения
interleaveПреобразование Callable
import itertools
from collections import defaultdict
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Набор данных
Похоже наArtificialDatasetВы можете создать набор данных, возвращая время, проведенное на каждом шаге.
class TimeMeasuredDataset(tf.data.Dataset):
# OUTPUT: (steps, timings, counters)
OUTPUT_TYPES = (tf.dtypes.string, tf.dtypes.float32, tf.dtypes.int32)
OUTPUT_SHAPES = ((2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3))
_INSTANCES_COUNTER = itertools.count() # Number of datasets generated
_EPOCHS_COUNTER = defaultdict(itertools.count) # Number of epochs done for each dataset
def _generator(instance_idx, num_samples):
epoch_idx = next(TimeMeasuredDataset._EPOCHS_COUNTER[instance_idx])
# Opening the file
open_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.03)
open_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - open_enter
for sample_idx in range(num_samples):
# Reading data (line, record) from the file
read_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.015)
read_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - read_enter
yield (
[("Open",), ("Read",)],
[(open_enter, open_elapsed), (read_enter, read_elapsed)],
[(instance_idx, epoch_idx, -1), (instance_idx, epoch_idx, sample_idx)]
)
open_enter, open_elapsed = -1., -1. # Negative values will be filtered
def __new__(cls, num_samples=3):
return tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(
cls._generator,
output_types=cls.OUTPUT_TYPES,
output_shapes=cls.OUTPUT_SHAPES,
args=(next(cls._INSTANCES_COUNTER), num_samples)
)
Этот набор данных предоставляет образцы формы[[2, 1], [2, 2], [2, 3]]и типа[tf.dtypes.string, tf.dtypes.float32, tf.dtypes.int32]Полем Каждый образец:
(
[("Open"), ("Read")],
[(t0, d), (t0, d)],
[(i, e, -1), (i, e, s)]
)
Где:
OpenиReadидентификаторы шаговt0это метка времени, когда начался соответствующий шагdэто время, проведенное на соответствующем этапеiэто индекс экземпляраeэто индекс эпохи (количество раз, когда набор данных был итератирован)sэто индекс образца
Итерационная петля
Сделайте петлю итерации немного сложнее, чтобы объединить все время. Это будет работать только с наборами данных, генерирующих образцы, как подробно описано выше.
def timelined_benchmark(dataset, num_epochs=2):
# Initialize accumulators
steps_acc = tf.zeros([0, 1], dtype=tf.dtypes.string)
times_acc = tf.zeros([0, 2], dtype=tf.dtypes.float32)
values_acc = tf.zeros([0, 3], dtype=tf.dtypes.int32)
start_time = time.perf_counter()
for epoch_num in range(num_epochs):
epoch_enter = time.perf_counter()
for (steps, times, values) in dataset:
# Record dataset preparation informations
steps_acc = tf.concat((steps_acc, steps), axis=0)
times_acc = tf.concat((times_acc, times), axis=0)
values_acc = tf.concat((values_acc, values), axis=0)
# Simulate training time
train_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.01)
train_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - train_enter
# Record training informations
steps_acc = tf.concat((steps_acc, [["Train"]]), axis=0)
times_acc = tf.concat((times_acc, [(train_enter, train_elapsed)]), axis=0)
values_acc = tf.concat((values_acc, [values[-1]]), axis=0)
epoch_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - epoch_enter
# Record epoch informations
steps_acc = tf.concat((steps_acc, [["Epoch"]]), axis=0)
times_acc = tf.concat((times_acc, [(epoch_enter, epoch_elapsed)]), axis=0)
values_acc = tf.concat((values_acc, [[-1, epoch_num, -1]]), axis=0)
time.sleep(0.001)
tf.print("Execution time:", time.perf_counter() - start_time)
return {"steps": steps_acc, "times": times_acc, "values": values_acc}
Метод графика
Наконец, определите функцию, способную построить временную шкалу, учитывая значения, возвращаемыеtimelined_benchmarkфункция
def draw_timeline(timeline, title, width=0.5, annotate=False, save=False):
# Remove invalid entries (negative times, or empty steps) from the timelines
invalid_mask = np.logical_and(timeline['times'] > 0, timeline['steps'] != b'')[:,0]
steps = timeline['steps'][invalid_mask].numpy()
times = timeline['times'][invalid_mask].numpy()
values = timeline['values'][invalid_mask].numpy()
# Get a set of different steps, ordered by the first time they are encountered
step_ids, indices = np.stack(np.unique(steps, return_index=True))
step_ids = step_ids[np.argsort(indices)]
# Shift the starting time to 0 and compute the maximal time value
min_time = times[:,0].min()
times[:,0] = (times[:,0] - min_time)
end = max(width, (times[:,0]+times[:,1]).max() + 0.01)
cmap = mpl.cm.get_cmap("plasma")
plt.close()
fig, axs = plt.subplots(len(step_ids), sharex=True, gridspec_kw={'hspace': 0})
fig.suptitle(title)
fig.set_size_inches(17.0, len(step_ids))
plt.xlim(-0.01, end)
for i, step in enumerate(step_ids):
step_name = step.decode()
ax = axs[i]
ax.set_ylabel(step_name)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.set_xlabel("time (s)")
ax.set_xticklabels([])
ax.grid(which="both", axis="x", color="k", linestyle=":")
# Get timings and annotation for the given step
entries_mask = np.squeeze(steps==step)
serie = np.unique(times[entries_mask], axis=0)
annotations = values[entries_mask]
ax.broken_barh(serie, (0, 1), color=cmap(i / len(step_ids)), linewidth=1, alpha=0.66)
if annotate:
for j, (start, width) in enumerate(serie):
annotation = "\n".join([f"{l}: {v}" for l,v in zip(("i", "e", "s"), annotations[j])])
ax.text(start + 0.001 + (0.001 * (j % 2)), 0.55 - (0.1 * (j % 2)), annotation,
horizontalalignment='left', verticalalignment='center')
if save:
plt.savefig(title.lower().translate(str.maketrans(" ", "_")) + ".svg")
Используйте обертки для функции сопоставления
Чтобы запустить карту функцию в нетерпеливом контексте, вы должны обернуть их вtf.py_functionвызов.
def map_decorator(func):
def wrapper(steps, times, values):
# Use a tf.py_function to prevent auto-graph from compiling the method
return tf.py_function(
func,
inp=(steps, times, values),
Tout=(steps.dtype, times.dtype, values.dtype)
)
return wrapper
Сравнение трубопроводов
_batch_map_num_items = 50
def dataset_generator_fun(*args):
return TimeMeasuredDataset(num_samples=_batch_map_num_items)
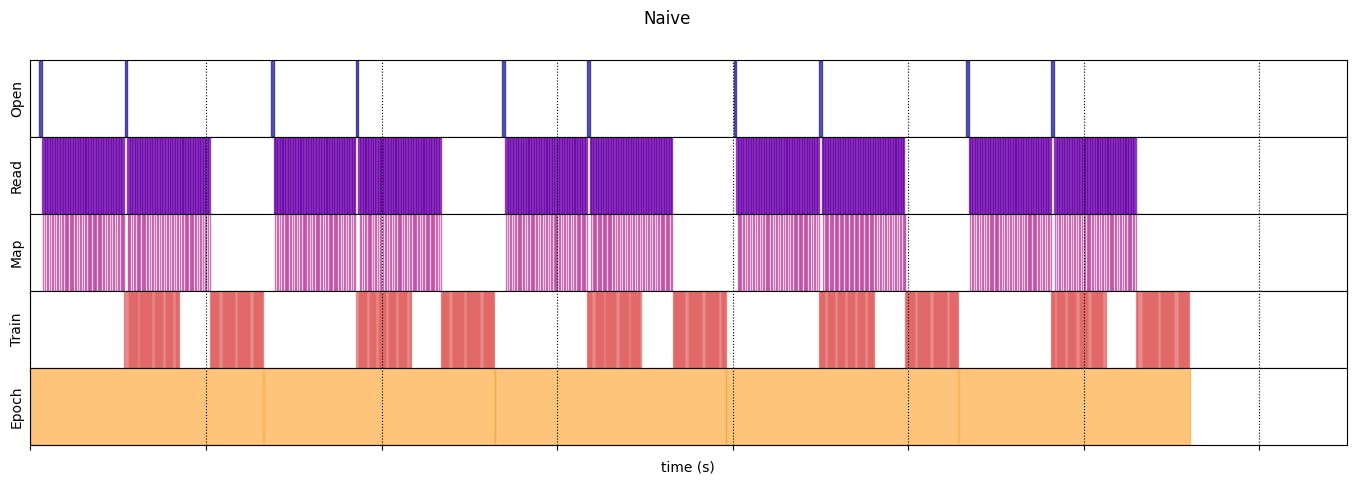
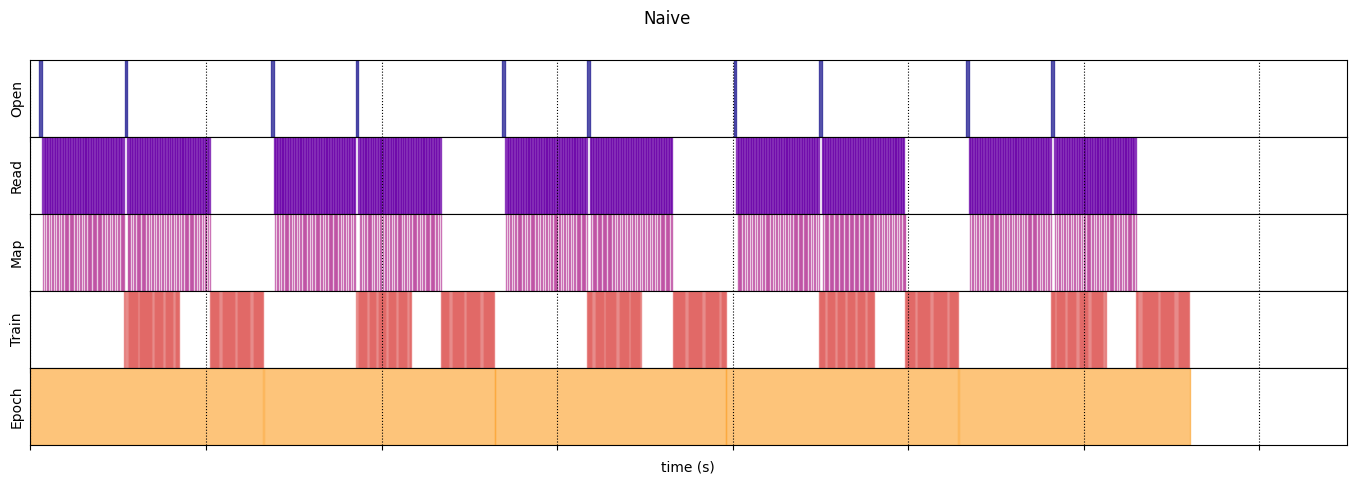
Наив
@map_decorator
def naive_map(steps, times, values):
map_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.001) # Time consuming step
time.sleep(0.0001) # Memory consuming step
map_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - map_enter
return (
tf.concat((steps, [["Map"]]), axis=0),
tf.concat((times, [[map_enter, map_elapsed]]), axis=0),
tf.concat((values, [values[-1]]), axis=0)
)
naive_timeline = timelined_benchmark(
tf.data.Dataset.range(2)
.flat_map(dataset_generator_fun)
.map(naive_map)
.batch(_batch_map_num_items, drop_remainder=True)
.unbatch(),
5
)
WARNING:tensorflow:From /tmpfs/tmp/ipykernel_112933/64197174.py:32: calling DatasetV2.from_generator (from tensorflow.python.data.ops.dataset_ops) with output_types is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
Instructions for updating:
Use output_signature instead
WARNING:tensorflow:From /tmpfs/tmp/ipykernel_112933/64197174.py:32: calling DatasetV2.from_generator (from tensorflow.python.data.ops.dataset_ops) with output_shapes is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
Instructions for updating:
Use output_signature instead
Execution time: 13.208576904999973
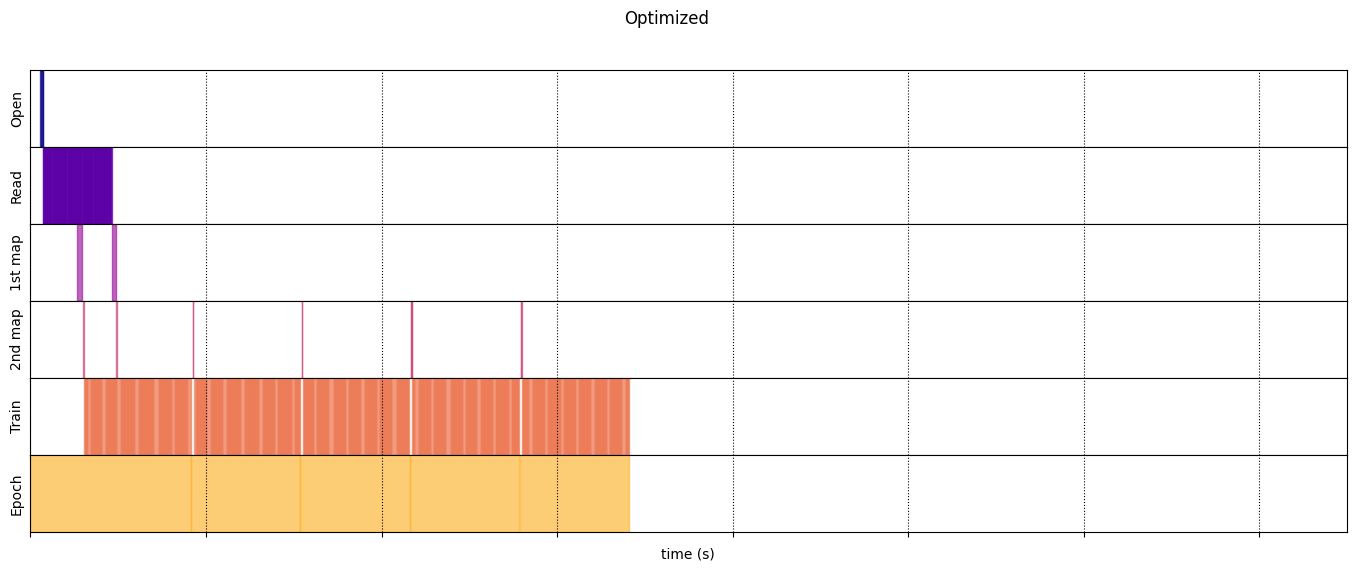
Оптимизированный
@map_decorator
def time_consuming_map(steps, times, values):
map_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.001 * values.shape[0]) # Time consuming step
map_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - map_enter
return (
tf.concat((steps, tf.tile([[["1st map"]]], [steps.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1),
tf.concat((times, tf.tile([[[map_enter, map_elapsed]]], [times.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1),
tf.concat((values, tf.tile([[values[:][-1][0]]], [values.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1)
)
@map_decorator
def memory_consuming_map(steps, times, values):
map_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.0001 * values.shape[0]) # Memory consuming step
map_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - map_enter
# Use tf.tile to handle batch dimension
return (
tf.concat((steps, tf.tile([[["2nd map"]]], [steps.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1),
tf.concat((times, tf.tile([[[map_enter, map_elapsed]]], [times.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1),
tf.concat((values, tf.tile([[values[:][-1][0]]], [values.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1)
)
optimized_timeline = timelined_benchmark(
tf.data.Dataset.range(2)
.interleave( # Parallelize data reading
dataset_generator_fun,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
.batch( # Vectorize your mapped function
_batch_map_num_items,
drop_remainder=True)
.map( # Parallelize map transformation
time_consuming_map,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
.cache() # Cache data
.map( # Reduce memory usage
memory_consuming_map,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
.prefetch( # Overlap producer and consumer works
tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
.unbatch(),
5
)
Execution time: 6.8234945540007175
draw_timeline(naive_timeline, "Naive", 15)
/tmpfs/tmp/ipykernel_112933/2966908191.py:17: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: The get_cmap function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.7 and will be removed in 3.11. Use ``matplotlib.colormaps[name]`` or ``matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap()`` or ``pyplot.get_cmap()`` instead.
cmap = mpl.cm.get_cmap("plasma")
draw_timeline(optimized_timeline, "Optimized", 15)
/tmpfs/tmp/ipykernel_112933/2966908191.py:17: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: The get_cmap function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.7 and will be removed in 3.11. Use ``matplotlib.colormaps[name]`` or ``matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap()`` or ``pyplot.get_cmap()`` instead.
cmap = mpl.cm.get_cmap("plasma")
Первоначально опубликовано на
Оригинал
